# Data model
GridDB is a unique Key-Container data model that resembles Key-Value. It has the following features.
- A concept resembling a RDB table that is a container for grouping Key-Value has been introduced.
- A schema to define the data type for the container can be set. An index can be set in a column.
- Transactions can be carried out on a row basis within the container. In addition, ACID is guaranteed on a container basis.
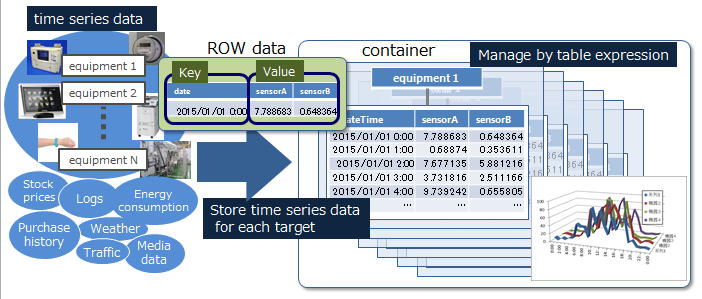
GridDB manages data in blocks, containers, tables, rows, and partitions.
Block
A block is a data unit for data persistence processing in a disk (hereinafter referred to a checkpoint) and is the smallest physical data management unit in GridDB. Multiple container data are arranged in a block. Block size is set up in a definition file (cluster definition file) before the initial startup of GridDB.
As a database file is created during initial startup of the system, the block size cannot be changed after initial startup of GridDB.
Container (Table)
A container is a data structure that serves as an interface with the user. A container consists of multiple blocks. Data structure serving as an I/F with the user. Container to manage a set of rows. It is called a container when operating with NoSQL I/F, and a table when operating with NewSQL I/F. 2 data types exist, collection (table) and timeseries container (timeseries table).
Before registering data in an application, there is a need to make sure that a container (table) is created beforehand. Data is registered in a container (table).
Row
A row refers to a row of data to be registered in a container or table. Multiple rows can be registered in a container or table but this does not mean that data is arranged in the same block. Depending on the registration and update timing, data is arranged in suitable blocks within partitions.
A row includes columns of more than one data type.
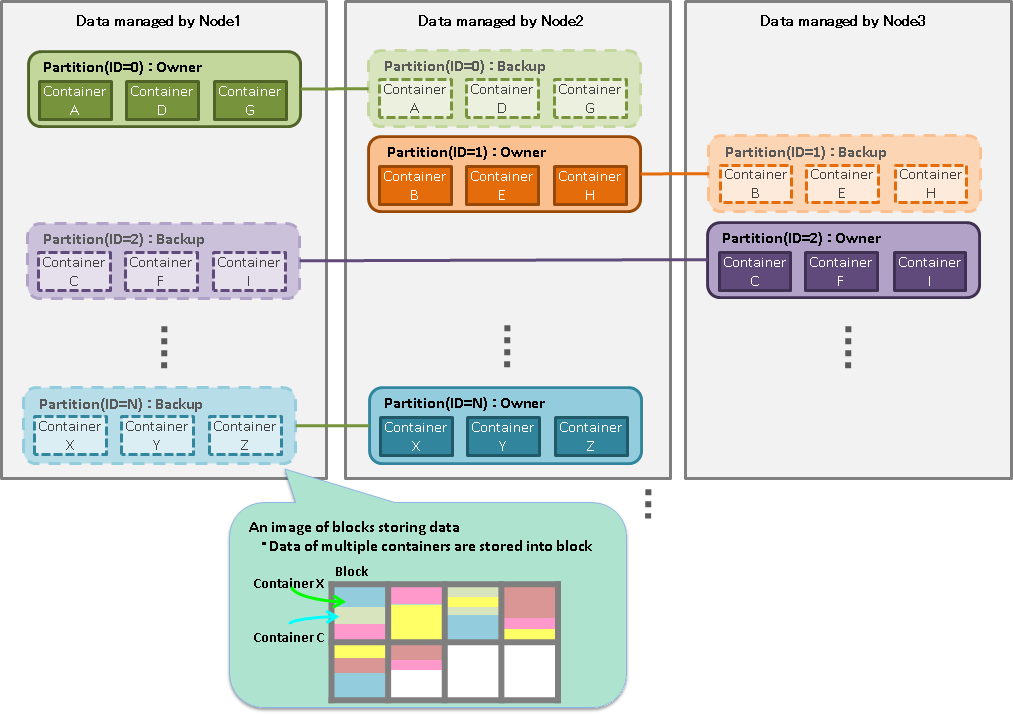
Partition
A partition is a data management unit that includes 1 or more containers or tables.
A partition is a data arrangement unit between clusters for managing the data movement to adjust the load balance between nodes and data multiplexing (replica) in case of a failure. Data replica is arranged in a node to compose a cluster on a partition basis.
A node that can update a container in a partition is called an owner node and one owner node is allocated to one partition. A node that maintains replicas other than owner nodes is a backup node. Master data and multiple backup data exist in a partition, depending on the number of replicas set.
The relationship between a container and a partition is persistent and the partition which has a specific container is not changed. The relationship between a partition and a node is temporary and the autonomous data placement may cause partition migration to another node.
Data retained by a partition is saved in an OS disk as a physical database file.
# Container
To register and search for data in GridDB, a container (table) needs to be created to store the data. Data structure serving as an I/F with the user. Container to manage a set of rows. It is called a container when operating with NoSQL I/F, and a table when operating with NewSQL I/F.
The naming rules for containers (tables) are the same as those for databases.
- A string consisting of alphanumeric characters, the underscore mark, the hyphen mark, the dot mark, the slash mark and the equal mark can be specified. The container name should not start with a number.
- Although the name is case sensitive, a container (table) cannot be created if it has the same name as an existing container when they are case insensitive.
[Notes]
- Avoid the name already used for naming a view in the same database.
# Type
There are 2 container (table) data types. A timeseries container (timeseries table) is a data type which is suitable for managing hourly data together with the occurrence time while a collection (table) is suitable for managing a variety of data.
# Data type
The schema can be set in a container (table). The basic data types that can be registered in a container (table) are the basic data type and array data type .
# Basic data types
Describes the basic data types that can be registered in a container (table). A basic data type cannot be expressed by a combination of other data types.
| JSON Data type | Description |
|---|---|
| BOOL | True or false |
| STRING | Composed of an arbitrary number of characters using the unicode code point |
| BYTE | Integer value from -27to 27-1 (8bits) |
| SHORT | Integer value from -215to 215-1 (16bits) |
| INTEGER | Integer value from -231to 231-1 (32bits) |
| LONG | Integer value from -263to 263-1 (64bits) |
| FLOAT | Single precision (32 bits) floating point number defined in IEEE754 |
| DOUBLE | Double precision (64 bits) floating point number defined in IEEE754 |
| TIMESTAMP | Data type expressing the date and time Data format maintained in the database is UTC, and accuracy is in milliseconds |
| GEOMETRY | Data type to represent a space structure |
| BLOB | Data type for binary data such as images, audio, etc. |
The following restrictions apply to the size of the data that can be managed for STRING, GEOMETRY and BLOB data. The restriction value varies according to the block size which is the input/output unit of the database in the GridDB definition file (gs_node.json).
| Data type | Block size (64KB) | Block size (from 1MB to 32MB) |
|---|---|---|
| STRING | Maximum 31KB (equivalent to UTF-8 encode) | Maximum 128KB (equivalent to UTF-8 encode) |
| GEOMETRY | Maximum 31KB (equivalent to the internal storage format) | Maximum 128KB (equivalent to the internal storage format) |
| BLOB | Maximum 1GB - 1Byte | Maximum 1GB - 1Byte |
GEOMETRY-type (Spatial-type)
GEOMETRY-type (Spatial-type) data is often used in map information system and available only for a NoSQL interface, not supported by a NewSQL interface.
GEOMETRY type data is described using WKT (Well-known text). WKT is formulated by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), a nonprofit organization promoting standardization of information on geospatial information. In GridDB, the spatial information described by WKT can be stored in a column by setting the column of a container as a GEOMETRY type.
GEOMETRY type supports the following WKT forms.
- POINT
- Point represented by two or three-dimensional coordinate.
- Example) POINT(0 10 10)
- LINESTRING
- Set of straight lines in two or three-dimensional space represented by two or more points.
- Example) LINESTRING(0 10 10, 10 10 10, 10 10 0)
- POLYGON
- Closed area in two or three-dimensional space represented by a set of straight lines. Specify the corners of a POLYGON counterclockwise. When building an island in a POLYGON, specify internal points clockwise.
- Example) POLYGON((0 0,10 0,10 10,0 10,0 0)), POLYGON((35 10, 45 45, 15 40, 10 20, 35 10),(20 30, 35 35, 30 20, 20 30))
- POLYHEDRALSURFACE
- Area in the three-dimensional space represented by a set of the specified area.
- Example) POLYHEDRALSURFACE(((0 0 0, 0 1 0, 1 1 0, 1 0 0, 0 0 0)), ((0 0 0, 0 1 0, 0 1 1, 0 0 1, 0 0 0)), ((0 0 0, 1 0 0, 1 0 1, 0 0 1, 0 0 0)), ((1 1 1, 1 0 1, 0 0 1, 0 1 1, 1 1 1)), ((1 1 1, 1 0 1, 1 0 0, 1 1 0, 1 1 1)), ((1 1 1, 1 1 0, 0 1 0, 0 1 1, 1 1 1)))
- QUADRATICSURFACE
- Two-dimensional curved surface in a three-dimensional space represented by defining equation f(X) = <AX, X> + BX + c.
The space structure written by QUADRATICSURFACE cannot be stored in a container, only can be specified as a search condition.
Operations using GEOMETRY can be executed with API or TQL.
With TQL, management of two or three-dimensional spatial structure is possible. Generating and judgement function are also provided.
SELECT * WHERE ST_MBRIntersects(geom, ST_GeomFromText('POLYGON((0 0,10 0,10 10,0 10,0 0))'))
See "GridDB TQL Reference" for details of the functions of TQL.
# HYBRID
A data type composed of a combination of basic data types that can be registered in a container. The only hybrid data type in the current version is an array.
Array
Expresses an array of values. Among the basic data types, only GEOMETRY and BLOB data cannot be maintained as an array. The restriction on the data volume that can be maintained in an array varies according to the block size of the database.
Data type Block size (64KB) Block size (from 1MB to 32MB) Number of arrays 4000 65000
[Note]
The following restrictions apply to TQL operations in an array column.
Although the i-th value in the array column can be compared, calculations (aggregation) cannot be performed on all the elements.
(Example) When columnA was defined as an array
The elements in an array such as select * where ELEMENT (0, column A) > 0 can be specified and compared. However, a variable cannot be specified instead of "0" in the ELEMENT.
Aggregation such as select SUM (column A) cannot be carried out.
# Primary key
A primary key can be set in a container (table), The uniqueness of a row with a set ROWKEY is guaranteed. NULL is not allowed in the column ROWKEY is set.
In NewSQL I/F, ROWKEY is called as PRIMARY KEY.
- For a timeseries container (timeseries table)
- A ROWKEY can be set in the first column of the row. (This is set in Column No. 0 since columns start from 0 in GridDB.)
- ROWKEY (PRIMARY KEY) is a TIMESTAMP
- Must be specified.
- For a collection (table)
- ROWKEY (PRIMARY KEY) can be set to multiple columns that are continuous from the first column. The ROWKEY set to multiple columns is called composite ROWKEY, which can be set up to 16 columns.
- Example) ROWKEY can be set to str1, str2, str3, which are consecutive from the first column.
CREATE TABLE sample_table1 (str1 string, str2 string, str3 string, str4 string, str5 string, int1 integer, PRIMARY KEY(str1, str2, str3)); - Example) ROWKEY can not be set to str1, str3, str4, which are not consecutive columns. Executing the following SQL will cause an error.
CREATE TABLE sample_table2 (str1 string, str2 string, str3 string, str4 string, str5 string, int1 integer, PRIMARY KEY(str1, str3, str4));
- Example) ROWKEY can be set to str1, str2, str3, which are consecutive from the first column.
- A ROWKEY (PRIMARY KEY) is either a STRING, INTEGER, LONG or TIMESTAMP column.
- Need not be specified.
- ROWKEY (PRIMARY KEY) can be set to multiple columns that are continuous from the first column. The ROWKEY set to multiple columns is called composite ROWKEY, which can be set up to 16 columns.
A default index prescribed in advance according to the column data type can be set in a column set in ROWKEY (PRIMARY KEY).
In the current version GridDB, the default index of all STRING, INTEGER, LONG or TIMESTAMP data that can be specified in a ROWKEY (PRIMARY KEY) is the TREE index.
[Notes]
- Refer to "Handling composite row keys" in "GridDB SQL Reference" for an example of setting composite row keys with NoSQL interface.
# View
View provides reference to data in a container.
Define a reference (SELECT statement) to a container when creating a view. A view is an object similar to a container, but it does not have real data. When executing a query containing a view, the SELECT statement, which was defined when the view was created, is evaluated, and a result is returned.
Views can only be referenced (SELECT), neither adding data (INSERT), updating (UPDATE), nor deletion data (DELETE) are not accepted.
[Notes]
- Avoid the name already used for naming a container in the same database.
- The naming rule of a view is the same as the naming rule of a container.
